Using Docker
- Docker
- 2023/02/20
1. Help
docker help
Common commands
run Create and run a new container from an image
exec Execute a command in a running container
ps List containers
build Build an image from a Dockerfile
pull Download an image from a registry
push Upload an image to a registry
images List images
login Log in to a registry
logout Log out from a registry
search Search Docker Hub for images
version Show the Docker version information
info Display system-wide information
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container
commit Create a new image from a container's changes
cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem
create Create a new container
diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem
events Get real time events from the server
export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive
history Show the history of an image
import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image
inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects
kill Kill one or more running containers
load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN
logs Fetch the logs of a container
pause Pause all processes within one or more containers
port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
rename Rename a container
restart Restart one or more containers
rm Remove one or more containers
rmi Remove one or more images
save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default)
start Start one or more stopped containers
stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics
stop Stop one or more running containers
tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE
top Display the running processes of a container
unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers
update Update configuration of one or more containers
wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit codes
Management commands
builder Manage builds
buildx* Docker Buildx (Docker Inc., v0.12.0-desktop.2)
compose* Docker Compose (Docker Inc., v2.23.3-desktop.2)
container Manage containers
context Manage contexts
dev* Docker Dev Environments (Docker Inc., v0.1.0)
extension* Manages Docker extensions (Docker Inc., v0.2.21)
feedback* Provide feedback, right in your terminal! (Docker Inc., 0.1)
image Manage images
init* Creates Docker-related starter files for your project (Docker Inc., v0.1.0-beta.10)
manifest Manage Docker image manifests and manifest lists
network Manage networks
plugin Manage plugins
sbom* View the packaged-based Software Bill Of Materials (SBOM) for an image (Anchore Inc., 0.6.0)
scan* Docker Scan (Docker Inc., v0.26.0)
scout* Docker Scout (Docker Inc., v1.2.0)
system Manage Docker
trust Manage trust on Docker images
volume Manage volumes
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
docker info |
|
docker version |
|
systemctl status docker |
The Docker service listens on this socket unix:///var/run/docker.sock |
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2023-12-10 09:16:45 AEDT; 1h 2min ago
TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket
Docs: https://docs.docker.com
Main PID: 12734 (dockerd)
Tasks: 11
Memory: 62.6M
CPU: 1.856s
CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service
└─12734 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Dec 10 09:16:38 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:38.637659743+11:00" level=info msg="detected 127.0.0.53 nameserver, assumi>
Dec 10 09:16:40 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:40.743295073+11:00" level=info msg="[graphdriver] using prior storage driv>
Dec 10 09:16:40 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:40.767945298+11:00" level=info msg="Loading containers: start."
Dec 10 09:16:41 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:41.662452038+11:00" level=info msg="Default bridge (docker0) is assigned w>
Dec 10 09:16:41 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:41.928064213+11:00" level=info msg="Loading containers: done."
Dec 10 09:16:42 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:42.170197693+11:00" level=info msg="Docker daemon" commit=311b9ff graphdri>
Dec 10 09:16:42 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:42.170259477+11:00" level=info msg="Daemon has completed initialization"
Dec 10 09:16:45 blue dockerd[12734]: time="2023-12-10T09:16:45.891901044+11:00" level=info msg="API listen on /run/docker.sock"
Dec 10 09:16:45 blue systemd[1]: Started Docker Application Container Engine.
Dec 10 10:00:35 blue dockerd[12734]: 2023/12/10 10:00:35 http2: server: error reading preface from client @: read unix /run/docker.soc>
2. Images
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
docker images -a |
|
docker images --digests |
Show Image digests as well. |
docker images -aq |
|
docker history <image id> |
Show history of an image |
docker pull <image id> |
|
docker pull -a <image id> |
|
docker pull <image id>:<tag> |
|
docker build . –t my-app:1.0 |
|
docker rmi <image id> |
Remove one or more images |
docker image rm amazonlinux |
Another way to remove a image |
docker image prune –a –f |
Remove all images including the dangling images ; -a: all; -f: force |
docker tag <image> my-image:1.0 |
|
docker inspect <image> |
Inspect an image |
docker manifest inspect ryandam/funbox |
|
docker image pull ubuntu:20.04 |
New syntax to pull an image |
docker image list --digests ubuntu:20.04 |
Show digest |
docker image history ubuntu:20.04 |
|
docker image remove ubuntu:20.04 |
An Image ID is checksum of local image. It is the checksum of a JSON config file of the image.
Saving an Image
cd /tmp/test
docker save ryandam/funbox -o funbox.tar
tar xvf funbox.tar
3. Containers
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
docker run <image id> |
|
docker run –d <image id> |
Run in detached mode |
docker run –it <image id> bash |
Run bash shell process in the container and connect to the Standard Input |
docker exec -it adoring_tu bash |
Connect to a executing container |
docker stop <container id> |
|
docker rm <container> |
|
docker container prune |
Remove all stopped containers |
docker start <container id> |
|
docker restart <container id> |
|
docker pull docker.io/ryandam/funbox@sha256:f8bd35cc40f6exxx |
Pull an image using digest. A Digest is created when an Image is pushed to registry. |
docker run --rm ubuntu cat /etc/os-release |
Run a container to execute a command. |
docker run --rm -it --platform linux/ppc64le ryandam/cmatrix |
Testing a container for a different platform |
4. Interacting with a container
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
docker ps |
|
docker ps –a |
|
docker logs <container id> |
|
docker exec -it <container id> bash |
Start a bash process inside a running container |
docker inspect <container id> |
|
docker inspect --format='{{.State.Pid}}' <container> |
Get Process ID |
docker run --entrypoint "/bin/sh" -it --name my-time-zone-converter mcp/time-zone-converter |
Overriding entry point |
5. Networking
| Command | What it does | |
|---|---|---|
docker inspect <container> |
Inspect container settings | |
docker inspect --format='{{.NetworkSettings.IPAddress}}' <container> |
IP address of the container | |
docker port ecstatic_mahavira |
List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container | |
docker top ecstatic_mahavira |
Display the running processes of a container | |
docker network inspect wordpress-network |
Inspect a network |
6. Persistence
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
docker volume create jenkins_home |
Create a volume |
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart=on-failure -v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17 |
Docker volume jenkins_home is automatically created. |
docker volume ls |
|
docker volume rm <test-vol> |
|
docker run -d --rm -p 80:80 -v /tmp/my_web_page:/usr/share/nginx/html nginx |
Share a host system directory with container. |
7. Metadata
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
docker image inspect --format='{{json .Config.Labels}}' myimage |
View image's labels |
8. Scenarios
1. Executing a process when creating a container
docker run ubuntu sleep 30
docker run ubuntu:23.04 cat /etc/*release*
A container is already running. how to start a new process in the same container?
docker run -it ubuntu bash
docker exec youthful_shannon cat /etc/*release*
2. Display the running processes of a container
➜ docker top 9f
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
1000 3579 3557 0 02:02 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/tini -- /usr/local/bin/jenkins.sh
1000 3606 3579 4 02:02 ? 00:04:25 java -Duser.home=/var/jenkins_home -Djenkins.model.Jenkins.slaveAgentPort=50000 -Dhudson.lifecycle=hudson.lifecycle.ExitLifecycle -jar /usr/share/jenkins/jenkins.war
- This is the view from host machine.
➜ docker exec -it 9f bash
# -w: wide output. Use this option twice for unlimited width.
➜ ps -ewwf
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
jenkins 1 0 0 02:02 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/tini -- /usr/local/bin/jenkins.sh
jenkins 7 1 3 02:02 ? 00:04:25 java -Duser.home=/var/jenkins_home -Djenkins.model.Jenkins.slaveAgentPort=50000 -Dhudson.lifecycle=hudson.lifecycle.ExitLifecycle -jar /usr/share/jenkins/jenkins.war
- When I connect to the container, and list the processes, it is the same view.
- However, the Process IDs are different.
2. Remove all containers & Images
# Remove all the running containers first before removing all the images.
docker stop $(docker ps -aq)
docker rm $(docker ps -aq)
docker rmi -f $(docker images -qa)
-a- Show all containers-q- Only display container IDs
3. Port mapping
# Maps port 80 on the host with port 8000 in the container.
# Maps /tmp/Jenkins on host with /var/Jenkins_home in the container.
docker run -p 80:8000 -p 50000:50000 -v /tmp/jenkins:/var/jenkins_home -u root jenkins/jenkins:lts
4. Docker volumes
- A Docker volume is like any other Docker object (Image, Container). It has an ID, name, and other properties.
- It can be created, attached, deleted.
docker volume create jenkins-volume
docker run --name volume-test \
-v jenkins-volume:/var/jenkins_home \
-d \
-u root \
-p 80:8080 -p 50000:50000 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
- Here, we mapped a Docker volume
jenkins-volumewith a directory/var/jenkins_home, which will be created when the container starts. - Anything written to the
/var/jenkins_homepersists even after this container is removed. - The volume can also be shared with other containers
Where does Docker keep the volumes?
docker inspect jenkins-volume
[
{
"CreatedAt": "2023-12-09T20:36:46Z",
"Driver": "local",
"Labels": null,
"Mountpoint": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/jenkins-volume/_data",
"Name": "jenkins-volume",
"Options": null,
"Scope": "local"
}
]
5. Bind mount
docker run --name bind-mount-test \
-v /tmp/jenkins:/var/jenkins_home \
-u root \
-p 80:8080 -p 50000:50000 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
6. Copy a file from Host machine to a container
docker cp items/file-from-host.txt my-container:/
7. Sharing volumes across containers
docker run --name volume-test \
-v jenkins-volume:/var/jenkins_home \
-u root \
-p 80:8080 -p 50000:50000 \
jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
- This uses a volume
jenkins-volume
docker run -it --name log_checker --volumes-from volume-test ubuntu
- Volumes can be shared using
--volumes-from(Mount volumes from the specified container(s)) option.
Now, log in to the ubuntu container. A directory /var/jenkins_home is already created and contains the files which is created by the volume-test container. Any changes happening in the volume-test container's /var/jenkins_home directory are visible in the ubuntu container.
Using networks
docker network --help
Usage: docker network COMMAND
Manage networks
Commands:
connect Connect a container to a network
create Create a network
disconnect Disconnect a container from a network
inspect Display detailed information on one or more networks
ls List networks
prune Remove all unused networks
rm Remove one or more networks
Run 'docker network COMMAND --help' for more information on a command.
Create a custom network
docker network create custom-network
docker network ls
docker network inspect custom-network
[
{
"Name": "custom-network",
"Id": "78a9b11a16fc5a1bbdde6bedb00378be635726c81e79cebfa798c1de62e45ef6",
"Created": "2023-12-09T21:14:44.369168821Z",
"Scope": "local",
"Driver": "bridge",
"EnableIPv6": false,
"IPAM": {
"Driver": "default",
"Options": {},
"Config": [
{
"Subnet": "172.18.0.0/16",
"Gateway": "172.18.0.1"
}
]
},
"Internal": false,
"Attachable": false,
"Ingress": false,
"ConfigFrom": {
"Network": ""
},
"ConfigOnly": false,
"Containers": {},
"Options": {},
"Labels": {}
}
]
- A subnet
172.18.0.0/16is created. - It is a Bridge network.
A Network Interface is also created on the host.
ifconfig
br-7722b4ffd202: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 172.18.0.1 netmask 255.255.0.0 broadcast 172.18.255.255
ether 02:42:c6:1a:a3:d7 txqueuelen 0 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Containers in a custom network can communicate with each other using hostnames.
Sample #1 - Wordpress, MySQL, MySQLAdmin containers in a custom network
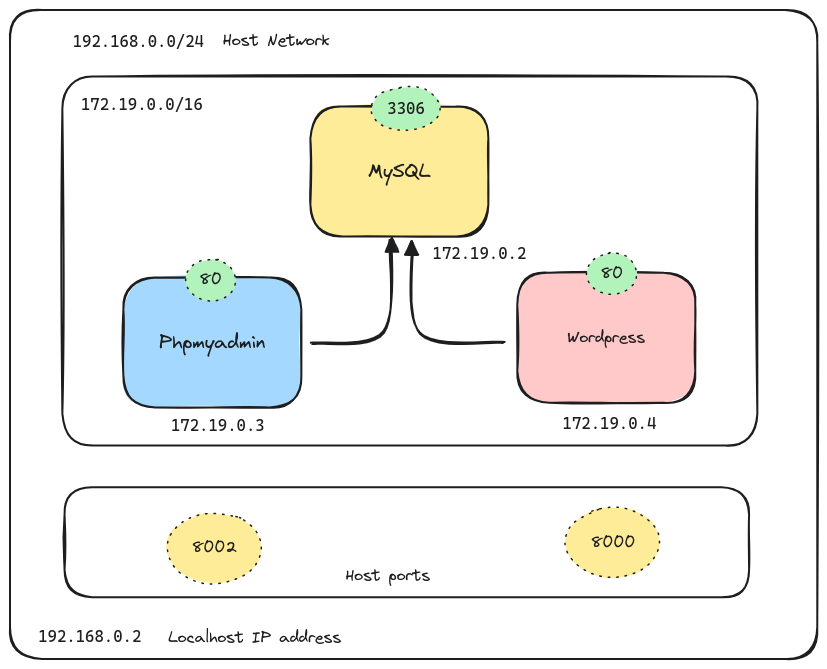
Create a network
docker network create wordpress-network
docker network ls
docker network inspect wordpress-network
MySQL container
- Wordpress needs a Database.
docker run \
--network wordpress-network \
--env MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=password \
--env MYSQL_DATABASE=wordpress \
--env MYSQL_USER=wordpress \
--env MYSQL_PASSWORD=password \
--name mysql \
--detach \
mysql
- The mysql container takes a minute to start the Database. monitor the logs using
docker logs <id> - When it is ready, there should be
ready for connectionsmessage.
Phpmyadmin container
# PMA_HOST - Host/Ip address of MySQL DB.
docker run \
--network wordpress-network \
--env PMA_HOST=mysql \
--publish 8002:80 \
--name phpadmin \
--detach \
phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
Wordpress container
docker run \
--network wordpress-network \
--publish 8000:80 \
--name wordpress \
--detach \
wordpress
How to limit resources given to a container?
Viewing any running container's usage
Running Jenkins server
https://github.com/jenkinsci/docker/blob/master/README.md
docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 --restart=on-failure -v jenkins_home:/var/jenkins_home jenkins/jenkins:lts-jdk17
- This will store the workspace in
/var/jenkins_home. All Jenkins data lives in there - including plugins and configuration. - This will automatically create a
jenkins_homedocker volume on the host machine. Docker volumes retain their content even when the container is stopped, started, or deleted.
Avoid using a bind mount from a folder on the host machine into
/var/jenkins_home, as this might result in file permission issues (the user used inside the container might not have rights to the folder on the host machine).
Error #1
I uninstalled Docker Desktop GUI App from my Ubuntu 22.04. then, I was getting this error - ERROR: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///home/ray/.docker/desktop/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running?
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44678725/cannot-connect-to-the-docker-daemon-at-unix-var-run-docker-sock-is-the-docker
- This is the way to properly uninstall Docker desktop - https://docs.docker.com/desktop/uninstall/
docker context ls
NAME DESCRIPTION DOCKER ENDPOINT ERROR
default Current DOCKER_HOST based configuration unix:///var/run/docker.sock
desktop-linux * Docker Desktop unix:///home/ray/.docker/desktop/docker.sock
Switch context to default.
docker context use default
default
Current context is now "default"
Cross compilation
To build images for different architectures.
docker buildx create --name buildx-multi-arch
docker buildx use buildx-multi-arch
docker login
docker buildx build --no-cache --platform linux/amd64,linux/arm64/v8 . -t ryandam/cmatrix --push
- This example creates an image for
linux/amd64,linux/arm64/v8.
2. Using Entrypoint & Cmd
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/#understand-how-cmd-and-entrypoint-interact
ENTRYPOINT has two forms - The exec form, which is the preferred form:
ENTRYPOINT ["executable", "param1", "param2"]
Command line arguments to
docker run <image>will be appended after all elements in an exec formENTRYPOINT, and will override all elements specified usingCMD.
Understand how CMD and ENTRYPOINT interact
Both CMD and ENTRYPOINT instructions define what command gets executed when running a container. There are few rules that describe their co-operation.
- Dockerfile should specify at least one of
CMDorENTRYPOINTcommands. ENTRYPOINTshould be defined when using the container as an executable.CMDshould be used as a way of defining default arguments for anENTRYPOINTcommand or for executing an ad-hoc command in a container.CMDwill be overridden when running the container with alternative arguments.
Sample
app.py
import sys
arg = sys.argv[1]
print(arg)
Dockerfile
FROM python:3.10
WORKDIR /
COPY ./app.py /
ENTRYPOINT ["python", "app.py"]
CMD ["hello"]
ENTRYPOINTis specified using exec form. It invokes a python script.CMDprovides a default argumenthello.
➜ docker run dockertest
➜ docker run dockertest "Hello world"
➜ docker run dockertest "Hello world, "
hello
Hello world
Hello world,
3. Using variables when building image
The ARG instruction defines a variable that users can pass at build-time to the builder with the docker build command using the --build-arg <varname>=<value> flag.
Dockerfile
FROM ubuntu
ARG CONT_IMG_VER=v1.0.0
RUN echo $CONT_IMG_VER
- A default value is provided to
CONT_IMG_VER
docker build --build-arg CONT_IMG_VER=v2.0.1 -t my-image .
- When building the image, a new value is supplied.